Cooling accounts for a large part of the energy used in data centers. It therefore plays a significant role in determining the sustainability of a data center facility. Here is an overview of how data center cooling innovations are improving the industry’s energy efficiency.
Liquid cooling solutions
Over recent years data centers have started to replace traditional air conditioning systems and cooling towers with more advanced liquid cooling solutions. These absorb and carry away heat much more effectively than their predecessors. This also means that they deliver the same (or better) results for much less power.
Currently, the two most popular liquid cooling solutions for data centers are direct-to-chip cooling and submersion cooling.
Direct-to-chip cooling: This involves the precise delivery of cold water through micro jets, strategically targeting the heat-generating areas on semiconductor chips. This method ensures efficient heat dissipation at the source.
Submersion cooling: This involves immersing servers in a non-conductive dielectric fluid, providing a highly efficient medium for heat dissipation. This minimizes the thermal resistance between the components and the cooling medium, leading to improved overall energy efficiency within data center operations.
The importance of liquid cooling systems has been recognized by the United States Department of Energy. Its “coolerchips” program funds diverse projects exploring liquid cooling technologies, with an emphasis on direct-to-chip cooling methods.
Airflow management strategies
Efficient airflow management is a critical aspect of optimizing data center cooling systems. By implementing effective airflow management, data center operators can significantly enhance their cooling efficiency. This reduces their energy consumption and hence contributes to a more sustainable operational model (and lower costs).
Proper airflow management positively impacts the partial power usage effectiveness (pPUE). This is a key metric for assessing the energy efficiency of data center operations. The reduction in pPUE signifies an improvement in overall energy utilization. This therefore highlights the significance of strategic airflow management in achieving substantial and measurable energy savings within the data center environment.
The basics of airflow management
Airflow management refers to guiding the flow of air through a location in a strategic manner. In a data center, it typically includes both the cold supply air and the hot exhaust air. This means that it essentially boils down to two basic principles. These are containment and direction.
Containment: The cold and hot air streams must be kept separate. If hot air mixes with cold air its cooling effectiveness will be compromised. Popular containment strategies include implementing hot/cold aisle containment, blocking open spaces under racks, and properly sealing openings in the raised floor.
Direction: Cold air must be strategically directed towards the IT equipment. Using perforated tiles, grommets, and blanking panels helps control the distribution of cold air to IT equipment and eliminates bypass airflow. For completeness, these strategies are most effective if a data center has a well-designed layout that contributes to minimizing air resistance and improving overall airflow.
Sustainable cooling practices
Sustainable practices are becoming pivotal in mitigating the environmental footprint of data centers. The need for sustainable data center cooling is also underscored by regulatory scrutiny and global efforts to align technological advancements with ecological responsibility. This is vital for ensuring the long-term viability of digital infrastructure without compromising environmental well-being.
Popular sustainable cooling practices
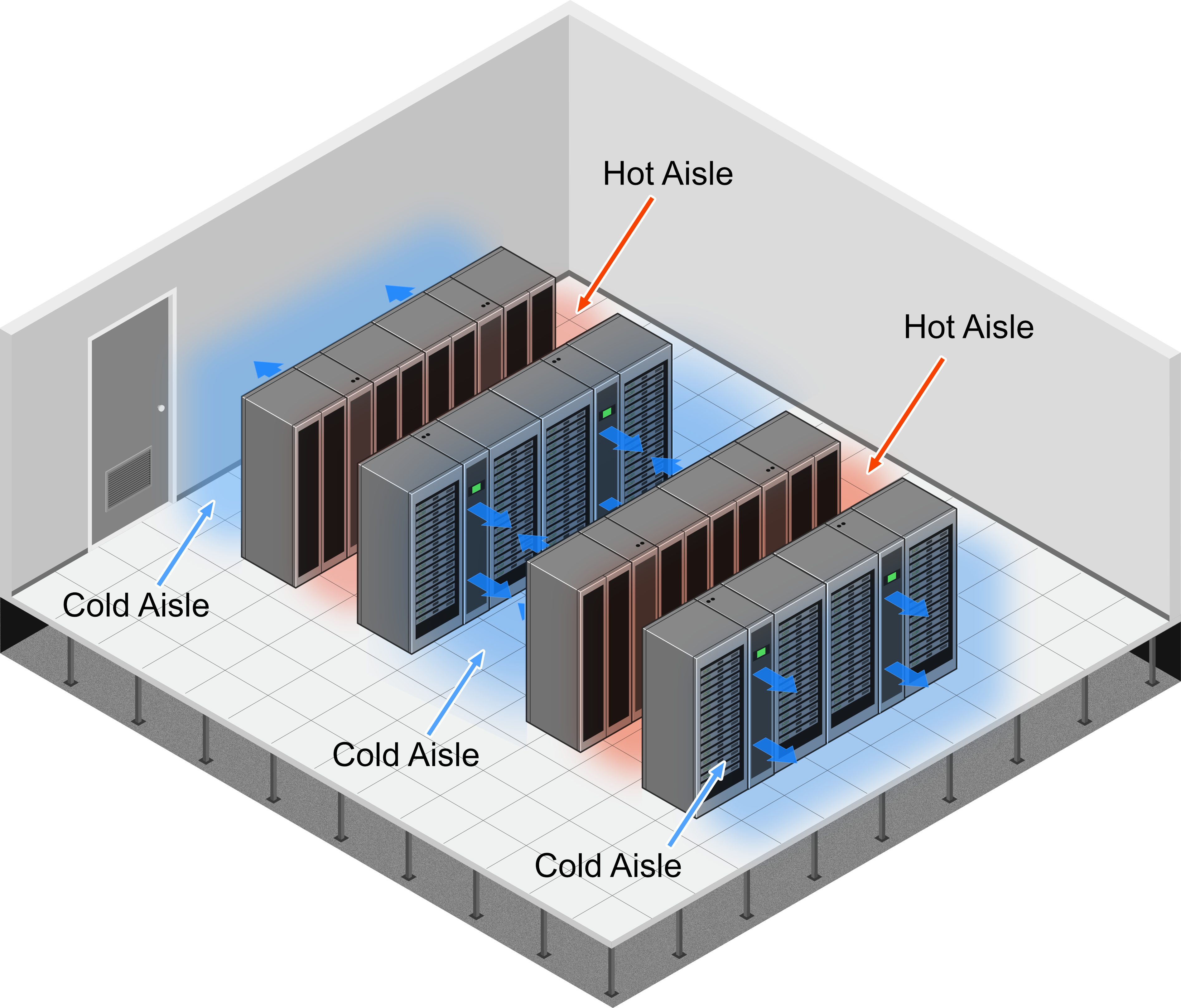
Hot/cold aisle containment: In this technique, server racks are arranged in alternating rows with cold air intakes facing one aisle and hot air exhausts facing the other. The cold aisle remains open and cold air is continuously directed into the server intakes. By contrast, the hot aisle is enclosed with containment structures such as doors and panels. This prevents the hot air from being recirculated before it is vented.
Free cooling: This leverages external environmental conditions to cool the facility. This is achieved through air-side or water-side economizers. Air-side economizers draw in cool air from the outdoors and circulate it through the data center. Water-side economizers use external water sources for cooling. The cool water absorbs heat from the data center, and the heated water is then discharged back to the external source.
Using renewable energy: This is not a substitute for reducing the amount of energy used by a data center. It can, however, be a significant complement to it. Ideally, the data center should generate some, if not all, of this energy itself (e.g. through solar panels and/or wind turbines).
The issue of water usage
In addition to reducing the energy consumption of cooling systems, it is also vital to reduce their water consumption. The emergence of water usage effectiveness (WUE) as a standard data center efficiency metric underscores the industry’s prioritization of sustainability.
WUE measures the amount of water used for cooling in relation to the energy consumption of a data center. A lower WUE indicates more efficient water usage. At present, this is often achieved by using reclaimed (waste) water and/or recycling water. The data center industry is also working to reduce the overall use of water for cooling.